What is Automation and How It Transforms Industries Today
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, automation stands at the forefront of industrial transformation, fundamentally altering how businesses operate and deliver value. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, automation has the potential to increase global productivity by up to 1.4 percent annually and could displace up to 375 million workers by 2030. Despite these challenges, the adoption of automation is seen as a critical driver for enhancing efficiency and competitiveness across various sectors.
The manufacturing industry, specifically, has been revolutionized by automation technologies, with a significant surge in the use of robotics and smart machinery. A study conducted by the World Economic Forum indicates that by 2025, around 85 million jobs may be displaced by shifts in labor between humans and machines, yet 97 million new roles could emerge that are more adapted to the new division of labor. This paradox highlights the necessity for industries to embrace automation not only to streamline workflows but also to reskill their workforce to meet the demands of a more automated future.
As businesses integrate automation into their processes, they can expect to witness not just cost savings, but also enhanced quality control, reduced time to market, and improved safety standards. The transformative power of automation paves the way for a more agile and innovative industrial landscape, promising a future where technology and human expertise work hand in hand.

Definition and Scope of Automation in Modern Industries
Automation has emerged as a pivotal force in modern industries, reshaping how businesses operate across various sectors. At its core, automation involves the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. This encompasses a range of tools and methodologies, from simple mechanical devices to complex algorithms powered by artificial intelligence. According to a report by McKinsey, approximately 60% of all occupations have at least 30% activities that could be automated, revealing a vast scope for efficiency improvements and cost reductions across industries.
In the manufacturing sector, for instance, automation can lead to significant enhancements in productivity and safety. The International Federation of Robotics (IFR) noted that global sales of industrial robots reached a record high of 384,000 units in 2020, a trend driven by the need for increased output and greater quality control. Beyond manufacturing, sectors such as logistics and healthcare are also embracing automation technologies. In logistics, the implementation of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can reduce operational costs by as much as 20%, while in healthcare, automation streamlines administrative tasks, allowing professionals to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork. This shift signifies a broader transformation where industries not only increase efficiency but also enhance the overall quality of services and products they deliver.
Historical Background: Evolution of Automation Technologies
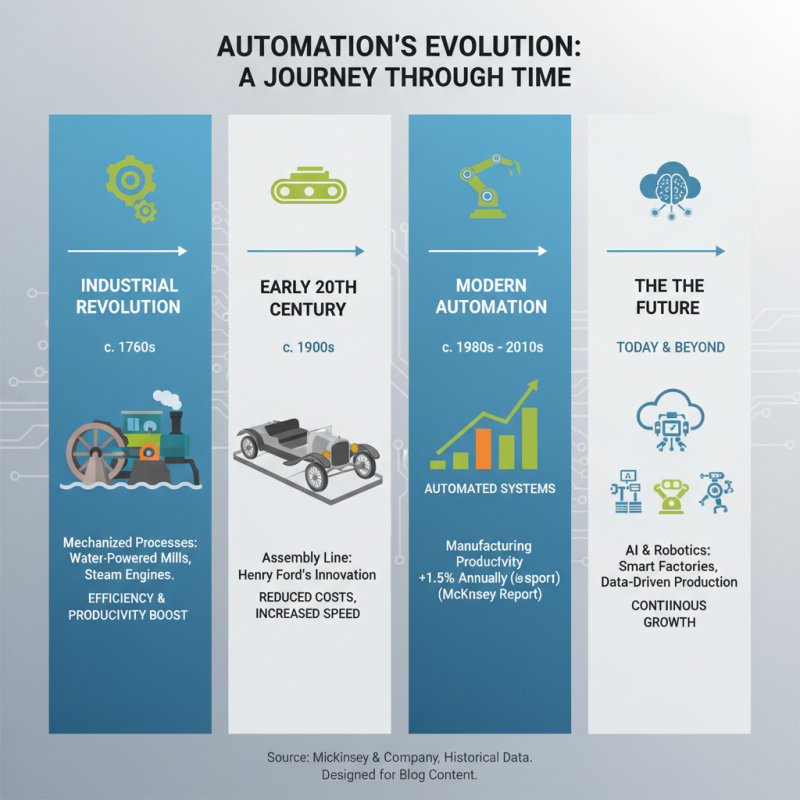
The historical evolution of automation technologies dates back to the Industrial Revolution, where the introduction of mechanized processes marked a significant shift in production methods. Early automated systems, such as water-powered mills and steam engines, greatly improved efficiency and productivity. By the early 20th century, assembly line techniques were developed, symbolized by Henry Ford's innovations, which reduced manufacturing costs and increased the speed of production. According to a report from McKinsey, the introduction of automation technologies in manufacturing led to a productivity increase of approximately 1.5% annually from 1980 to 2010.
The late 20th century and early 21st century saw the advent of digital automation and advanced robotics, which transformed industries such as automotive and electronics. The International Federation of Robotics reported that in 2020, the global stock of operational industrial robots reached 2.7 million units, signifying a remarkable 12% increase from the previous year. This surge in automation adoption has driven businesses to enhance their operational efficiency and reduce human error, with some sectors experiencing labor productivity gains of over 20% due to automation initiatives.
As we now navigate the era of Industry 4.0, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) into manufacturing processes is further propelling the evolution of automation technologies. A report by the World Economic Forum indicates that by 2025, 85 million jobs may be displaced by a shift in labor between humans and machines, while 97 million new roles could emerge. This ongoing transformation underscores the critical need for industries to adapt and evolve to leverage automation's full potential.
Key Technologies Driving Automation Today
Automation is rapidly transforming industries through the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA). According to a report by McKinsey, up to 45% of the activities that individuals are paid to perform can be automated using currently demonstrated technology. This shift not only enhances operational efficiency but also increases productivity, enabling organizations to reallocate resources toward more strategic tasks.
Key technologies driving automation today include AI algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data to inform decision-making processes, and RPA tools that carry out repetitive tasks without human intervention. For instance, the World Economic Forum predicts that by 2025, automation could displace 85 million jobs globally, but it is also expected to create 97 million new roles that are better suited to the new division of labor between humans, machines, and algorithms. Furthermore, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices enables real-time data collection and remote monitoring, streamlining operations across various sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. This evolution highlights the critical role of emerging technologies in reshaping how businesses operate and respond to market demands.
What is Automation and How It Transforms Industries Today - Key Technologies Driving Automation Today
| Technology | Description | Industries Impacted | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Software robots handling repetitive tasks in digital processes. | Finance, HR, Customer Service | Increased efficiency, Reduced operational costs |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine learning algorithms that analyze data to make decisions. | Healthcare, Retail, Logistics | Improved decision making, Enhanced customer experience |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Network of connected devices that collect and exchange data. | Manufacturing, Agriculture, Smart Cities | Real-time monitoring, Predictive maintenance |
| Cloud Computing | On-demand computing services over the internet. | IT, Education, Financial Services | Scalability, Cost savings, Flexibility |
| Machine Learning | Algorithms that improve automatically through experience. | Finance, Marketing, Cybersecurity | Enhanced analytics, Fraud detection |
Impacts of Automation on Workforce and Employment
Automation has a profound impact on the workforce and employment landscape across various industries. With the advent of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and machine learning, traditional job roles are being reshaped. Many tasks that once required human intervention are now being performed by machines, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. However, this shift raises concerns about job displacement, as workers in roles susceptible to automation may find themselves at risk of unemployment.
While automation can eliminate certain jobs, it also creates new opportunities within the labor market. There is a growing demand for professionals with skills in technology, data analysis, and system management. Jobs focused on maintaining and improving automated systems will emerge, requiring a workforce that is adaptable and well-versed in these technologies. As industries harness the benefits of automation, the dynamic of employment will evolve, emphasizing the need for continuous learning and skill development.
In this new era, flexibility and an open mindset will be crucial for workers to thrive amidst the changing employment landscape.
Case Studies: Automation Transforming Specific Industries
Automation has become a pivotal force in transforming various industries, as demonstrated by numerous case studies. In the manufacturing sector, for instance, a report from the World Economic Forum highlights that companies implementing automation technologies can increase productivity by up to 30%. This surge in efficiency is largely due to the adoption of robotics and artificial intelligence, which streamline operations and reduce human error. Factories equipped with automation are not only able to maintain production levels during labor shortages but also respond more swiftly to market demands.
In healthcare, automation has shown significant potential in improving patient care and operational efficiency. According to a study conducted by Deloitte, 32% of healthcare executives reported increased patient satisfaction due to automated scheduling and telemedicine capabilities. This shift not only reduces waiting times but also allows healthcare professionals to focus more on direct patient care rather than administrative tasks. The integration of health bots and automated systems has also led to a 15% reduction in operational costs for many organizations, enhancing overall service delivery.
**Tip:** To successfully implement automation in your industry, consider starting with a pilot program to measure impacts and refine processes before a full-scale roll-out.
**Tip:** It’s crucial to involve employees in the automation transition; their insights can lead to better integration and higher acceptance rates among the team.
Related Posts
-

How to Leverage Automation in 2025 for Business Success
-

10 Essential Automation Tips to Boost Your Productivity Today
-

Exploring the Future of Automation Catalogue for Streamlined Business Efficiency
-

Why Automation Help Streamline Your Business Operations and Save Time
-

10 Best Software Connect Solutions for Seamless Integration and Efficiency
-

Top 10 Software Connect Solutions for Seamless Integration and Collaboration